The paleo/low-carb world loves to cry about the relative quality of different dietary fats and how they relate to health. They reject the scientific consensus that states that saturated fat (SFA) contributes to cardiovascular disease risk (CVD). Their primary arguments essentially revolve around the notion that we have inadequate data to demonstrate that SFA increases CVD risk. Some will even go so far as to say that SFA is uniquely protective against CVD due to its ability to protect low density lipoprotein particles (LDL) from oxidation. Let's explore these claims.
1) Saturated Fat and Cardiovascular Disease
These arguments usually rely heavily on meta-analyses showing no effect of substituting PUFA for SFA on CVD risk in RCTs. But, ultimately these papers are typically just examples of meta-analysis methods being mangled and abused to serve a narrative. Let's look at the typical meta-analyses cited by paleo/low-carb people [1][2][3][4][5]. If we take the time to pick through them it doesn't take long to discover the problem. The methods and inclusion criteria are structured such that highly confounded or otherwise weak studies get lumped in with the high quality studies that are better controlled.
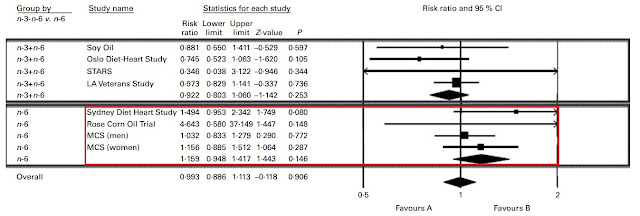
Trials that were unacceptably confounded, like the Sydney Diet Heart Study and the Minnesota Coronary Experiment, manage to sneak their way in. Both of these trials made no delineation between polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and trans-fats. Other trials with pathetically small amounts of statistical power, like the Rose Corn Oil Trial (n=41 lol), also manage to show up with a shocking amount of weight. If we jam enough weak or poorly controlled trials into our meta-analysis, they will offset the effects observed in the stronger trials and pull our effect toward a null result.
Needless to say, this is ridiculous. The continuous use of these flawed methods creates a sort of Groundhog Day effect that will leave us seeing the same shitty results over and over. Clearly we need better inclusion criteria and better statistical analyses to suss this out. Most meta-analyses aren't actually asking the most pertinent question— can rates of CVD-related mortality be predicted by the degree of LDL-lowering achieved by replacing SFA with PUFA? When we actually investigate the data while taking into account the relevant chain of causality, which is SFA -> LDL -> CVD, we actually see the effect in full swing [6].
Silverman, et al, did a great job of sussing this out. When the data is analyzed in this fashion, we see that reductions in CVD-related mortality are actually perfectly predicted by the degree of LDL-lowering achieved by replacing SFA with PUFA. Using LDL as the moderator variable in the meta-regression, we see that the interventions actually did reduce CVD commensurate with LDL-lowering. Not really a big surprise.
But they also take it a step further and plug the diet trials in alongside a number of other trials using different sorts of LDL-lowering interventions in another meta-regression. We see that the reductions in CVD-related mortality are perfectly predicted by the degree of LDL-lowering relative to other methods of LDL-lowering. The diet trials are exactly where we would expect them to be on the continuum of risk based on the LDL lowering achieved.
Let's look at the trials that met the inclusion criteria in this paper [7][8][9][10]. Notice anything interesting? That's right. These are the trials that typically get cancelled out by weaker trials in the silly-ass meta-analyses that I mentioned earlier.
The results discovered by Silverman, et al, are what we see when we strip away all of the weaker trials that don't belong in the analysis to begin with. This is what happens when we employ a laser-focused inclusion criteria and sound analysis methods.
Some people might say that the inclusion criteria in this meta-regression is too narrow, and that it is not fair to exclude the other classic fatty acid substitution trials. Interestingly enough, another meta-regression was just published a couple of days ago that includes virtually all of the classic fatty acid substitution trials [11]. Here are the pooled results.
Interesting findings. They are actually perfectly consistent with the guidelines to keep SFA below 10% of calories. We understand that the threshold of effect for SFA is a chronic consumption in excess of approximately 26-30g/day. This is why the guidelines tell us to stay under 10% of calories as SFA, because 10% of a 2000-2500 calorie diet is about 22-27g/day. 10% of calories is just a guideline to keep us under that threshold.
The findings of this second meta-regression also cohere with prospective cohort data when SFA is measured across cohorts as a percentage of calories [12]. Paleo quacks at this point might feel inclined to point out that there are some meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies that find no association between SFA and CVD mortality [13]. But, ultimately it just depends on how we choose to analyze the data, and what data we choose to include.
If we're just pooling median CVD mortality risk between countries based on within-population SFA intake, it's easy to understand how null results are possible. Not all populations are the same. Let me explain.
In America and Europe virtually everyone is eating >30g/day of SFA even in the lowest intake groups [14][15]. In China and Japan virtually everyone is eating <20g/day of SFA even in the highest intake groups [16][17][18]. So of course the relative risk is low or null within or between populations. This is because we're comparing high intakes versus high intakes and low intakes versus low intakes rather than genuinely measuring low versus high.
Take a look at the previous graph. The relative risk of CVD does not seem to increase once one's SFA intake goes beyond 10% of calories (approximately 22-27g/day). So naturally, meta-analyses that are not taking this into consideration will be vulnerable to missing the effect in their results. We need to measure low intakes versus high intakes. Period.
When we dig into the prospective cohort meta-analyses, we see the effect clear as day in cohorts that actually do have a wider range of intake [19][20][21]. We see studies that show intakes ranging from 14-40g/day (Mann, et al) of SFA rather than 30-60g/day of SFA or 7-18g/day of SFA. We see a step-wise increase in CVD-related mortality as a function of SFA intake in those particular cohorts. To hammer this point home, I conducted my own meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies based on my own inclusion/exclusion criteria. You can read more about that here.
But, this is what we see when we are not just comparing high intakes versus high intakes or low intakes versus low intakes and ignoring the threshold effect mentioned above. This is what we see when we are genuinely comparing low intakes versus high intakes in populations that are also crossing the threshold of effect within the range of intake. As a consequence, we see big differences in the relative risk of CVD mortality within those cohorts.
We do also have at least one case of an entire population shifting their average SFA intake from high to low, and seeing massive population-level reductions in CVD-related mortality [22][23].
From 1972-1985, this Finnish population dropped their CVD mortality rates by approximately 30%. The majority of this effect was attributable to the population substituting margarine for butter. Smoking rates did not change much and average BMI actually increased during this time. Back then, the decrease in mortality was attributed to measured reductions in total cholesterol across the population. However, in retrospect we can understand that it was likely the reductions in LDL that followed from ditching the butter.
2) Saturated Fat and LDL Oxidation
At this point we can say with confidence that SFA generally increases CVD risk in humans. But let's explore this idea that SFA uniquely protects LDL from oxidation. As it turns out, this question has actually been investigated from multiple angles. We've actually studied the effect of SFA, monounsaturated fat (MUFA), and PUFA on LDL oxidation [24][25][26].
On balance, there is little to no differential effect of SFA on the lag-time to LDL oxidation when compared to MUFA, and MUFA-rich diets might actually be more protective than SFA-rich diets. While it is true that the PUFA content determines an LDL particle's capacity for potential oxidation, the actual lag-time to oxidation is largely determined by the total antioxidant content of the fat itself [27][28][29][30].
Flax oil, hemp oil, almond oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, perilla oil, and rapeseed oil are all high-PUFA oils and their effects on LDL oxidation have been studied in detail [31][32][33][34][35][36]. The net effect of these oils is either to have no effect on the rate of LDL oxidation or to decrease the rate of LDL oxidation. It would appear that an LDL particle's susceptibility to oxidation has less to do with PUFA and more to do with antioxidant content of the fats being consumed.
In addition to increasing the lag time to LDL oxidation, the polyphenols found in these plant-derived oils could also be lowering the total amount of LDL particles through a threefold mechanism, independent of PUFA. Firstly, plant polyphenols may increase hepatic LDL receptor activity in certain cases [37]. Secondly, plant polyphenols may inhibit cholesterol uptake in the gut in certain cases [38]. Thirdly, increasing an LDL particles's resistance to oxidation may increase its binding affinity for LDL receptors and thus lower total LDL [39][40].
This could also provide us with a hint as to why animal fats seem to have such a pronounced effect on both LDL oxidation as well as LDL levels in general [41][42]. Animal fats are as close to isolated fatty acids as you can get in the human diet. Animal fats contain no polyphenols and they have very few antioxidant nutrients, like vitamin E, on average. So, animal fats in general seem to do very little to protect against LDL oxidation or mitigate the LDL-raising effects of SFA.
3) Saturated Fat from Animal Foods
This may seem like specious speculation on my part, however we have actual population-level outcome data supporting the view that animal-derived fats, particularly SFA, are uniquely problematic [43][44][45][46][47]. We also have a lot of data suggesting that many plant sources of SFA may be either neutral or beneficial for LDL and CVD risk, especially when compared to animal-derived SFA [48][49][50][51]. Even coconut oil seems to lower LDL went compared to butter, despite having 30% more SFA by weight.
All together it paints a pretty grim picture for animal-derived fats in general. Suggesting that even if it is the case that SFA uniquely protects LDL from oxidation, it may not be enough to offset the consequences of raising total LDL. Which in turn suggests that even if PUFA increases the rate of LDL oxidation, it doesn't appear to be enough to offset PUFA's LDL-lowering benefits.
In short, if MUFA protects LDL from oxidation to the same degree as SFA (if not better), why prefer SFA at all? SFA seems to offer no unique advantages and is at best a liability for CVD in and of itself. However, it seems that if you must choose a SFA-rich oil, plant-derived oils are very likely superior to animal-derived oils due to how the polyphenols may affect lipid metabolism. It may be true that SFA protects LDL from oxidation. In fact, it is true. But, it is no less true for MUFA, and MUFA might be better at it than SFA. So, why not simply prefer plant-derived MUFA and PUFA overall, and maybe don't sweat the plant-derived SFA in your diet as much.
As an ironic side-note, SFA specifically from cheese seems to have neutral or beneficial effects on LDL as well [52]. I say "ironic" because within the paleo diet's canon, dairy is generally off limits. But, if the paleo/low-carb folks wish to claim a victory in this regard, it would appear that there are also SFA-rich animal foods that don't seem to perturb LDL. But as far as I can tell this effect is strictly related to dairy fat that has not undergone homogenization [53]. This is likely due to the effect of the milk fat globule membrane. This membrane creates a food matrix that appears to mitigate the LDL-raising effects of the SFA.
4) Linoleic Acid and Cardiovascular Disease
Lastly, there is one additional claim made by paleo/low-carb folks that we should probably investigate as well. The claim that unsaturated oils high in linoleic acid (LA), a plant-derived omega-6 fatty acid, cause CVD. Support for this claim seems to be limited to narrative reviews made by whole-food purists who've somehow managed to get their bullshit published [54]. But let's take a look at the data before we wrap this up.
We already know from what we've discussed above that, generally speaking, SFA restriction leads to reductions in CVD mortality on a population level. But how does LA contribute to CVD risk in isolation? A meta-analysis (with imperfect but albeit better inclusion criteria than most meta-analyses on this topic) on fatty acid substitution RCTs sought to investigate the relationship between LA consumption and coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality and myocardial infarction (MI) [55].
Right off the bat, there are a couple confounded trials we can do away with. Again, the Minnesota Coronary Experiment needs to go. The Finnish Mental Hospital Study also needs to go due to the fact that it wasn't a true RCT and there was potential confounding due to different patient care and differing usages of pharmaceuticals between hospitals.
Nevertheless, even just eyeballing the damn forest plot it would be obvious that even with the omission of those two trials, the aggregated result would heavily favour PUFA. Just for fun, let's make our own forest plot to see the results.
The results favour replacing SFA with PUFA. The replacement yields an 18% reduction in risk, and is statistically significant (P=0.006). But how might this play out in the real world? These RCTs are investigating fatty acid substitutions by dumping isolated fatty acids on top of existing diets. People eat food. So, can we investigate the effect of LA on a population just eating foods and living their normal lives?
Epidemiological findings would seem to support the hypothesis that dietary LA confers reductions in CVD mortality [56]. But if you're one of those whacky paleo/low-carb people who absolutely hates nutritional epidemiology due to the supposed unreliability of food frequency questionnaires, you're in luck! Researchers who were aware of this potential issue said screw food frequency questionnaires. They just looked at tissue LA as a direct proxy for intake, and related LA representation in various tissues to CVD mortality [57]. Nice and tidy.
Colour me quirky, but that does not look like an agent of cardiovascular destruction to me.
One possible rebuttal at this point would be to suggest that this could merely be a reflection of healthy dietary habits, due to the fact that public health and nutrition guidelines have spent decades trumpeting for PUFA. This is known as the "healthy-user bias." It's certainly a plausible explanation. Except that the data seen above includes cohorts from non-English speaking countries that did not have dietary guidelines making any specific recommendations toward fat other than to limit it [58].
So, while the explanation is plausible, it may not actually be very likely. The healthy user bias cannot explain these results. Especially since, at least ostensibly, it would appear that those whose behaviours were at odds with the guidelines (by consuming more dietary fat and not less) actually had better health outcomes if their dietary fats were LA-rich. A truly hilarious amount of mental gymnastics would be required to explain these results.
In conclusion, as a general effect SFA consumption above a threshold of 10% of calories (or 22-27g/day) increases CVD risk in humans through increases in LDL. However, there are SFA-rich foods that can lower LDL and CVD risk due to mitigating factors such as fibre, polyphenols, or unique characteristics of the food matrix itself. It would also appear that dietary LA has an independent beneficial effect on CVD mortality, based on multiple lines of evidence spanning the entire evidence hierarchy. Sorry to say, but this is one situation where the dietary guidelines appear to be correct.
PS. If you like what you've read and want me to continue writing, consider supporting me on Patreon. Every little bit helps! Thank you for reading!
References:
[1] Christopher E Ramsden, et al. n-6 Fatty Acid-Specific and Mixed Polyunsaturate Dietary Interventions Have Different Effects on CHD Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Br J Nutr. 2010 Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21118617/
[2] Christopher E Ramsden, et al. Use of Dietary Linoleic Acid for Secondary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease and Death: Evaluation of Recovered Data From the Sydney Diet Heart Study and Updated Meta-Analysis. BMJ. 2013 Feb. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23386268/
[3] Christopher E Ramsden, et al. Re-evaluation of the Traditional Diet-Heart Hypothesis: Analysis of Recovered Data From Minnesota Coronary Experiment (1968-73). BMJ. 2016 Apr. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27071971/
[4] Zoë Harcombe, et al. Evidence From Randomised Controlled Trials Does Not Support Current Dietary Fat Guidelines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Heart. 2016 Aug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27547428/
[5] Steven Hamley. The Effect of Replacing Saturated Fat With Mostly n-6 Polyunsaturated Fat on Coronary Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutr J. 2017 May. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28526025/
[6] Michael G Silverman, et al. Association Between Lowering LDL-C and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Among Different Therapeutic Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27673306/
[7] Morris, et al. Controlled Trial of Soya-Bean Oil in Myocardial Infarction. Lancet. 1968 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4175085/
[8] S Dayton, et al. Controlled Trial of a Diet High in Unsaturated Fat for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Complications. Lancet. 1968 Nov. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4176868/
[9] P Leren. The Effect of Plasma Cholesterol Lowering Diet in Male Survivors of Myocardial Infarction. A Controlled Clinical Trial. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5228820
[10] Research Committee. Low-fat Diet in Myocardial Infarction: A Controlled Trial. Lancet. 1965 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4158171/
[11] Lee Hooper, et al. Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 19 May 2020. https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD011737.pub2/full
[12] Marianne U Jakobsen, et al. Major Types of Dietary Fat and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Pooled Analysis of 11 Cohort Studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 May. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19211817/
[13] Patty W Siri-Tarino, et al. Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies Evaluating the Association of Saturated Fat With Cardiovascular Disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20071648/
[14] Margret Leosdottir, et al. Cardiovascular Event Risk in Relation to Dietary Fat Intake in Middle-Aged Individuals: Data From The Malmö Diet and Cancer Study. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007 Oct. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17925631/
[15] Kyungwon Oh, et al. Dietary Fat Intake and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Women: 20 Years of Follow-Up of the Nurses' Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2005 Apr. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15781956/
[16] H Y Lee, et al. Serum Fatty Acid, Lipid Profile and Dietary Intake of Hong Kong Chinese Omnivores and Vegetarians. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000 Oct. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11083485/
[17] H Kato, J Tillotson, et al. Epidemiologic Studies of Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke in Japanese Men Living in Japan, Hawaii and California. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Jun. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4713933/
[18] Kenji Wakai, et al. Dietary Intakes of Fat and Total Mortality Among Japanese Populations With a Low Fat Intake: The Japan Collaborative Cohort (JACC) Study. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24597664/
[19] J I Mann, et al. Dietary Determinants of Ischaemic Heart Disease in Health Conscious Individuals. Heart. 1997 Nov. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9415002/
[20] Jiaqiong Xu, et al. Dietary Fat Intake and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: The Strong Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17023718/
[21] A Ascherio, et al. Dietary Fat and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Men: Cohort Follow Up Study in the United States. BMJ. 1996 Jul. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8688759/
[22] Erkki Vartiainen, et al. Thirty-five-year Trends in Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Finland. Int J Epidemiol. 2010 Apr. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19959603/
[23] Erkki Vartiainen. The North Karelia Project: Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Finland. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2018 Jun. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30083543/
[24] P Mata, et al. Effect of Dietary Fat Saturation on LDL Oxidation and Monocyte Adhesion to Human Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996 Nov. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8911273/
[25] U S Schwab, et al. The Effect of Quality and Amount of Dietary Fat on the Susceptibility of Low Density Lipoprotein to Oxidation in Subjects With Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998 Jun. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9683400/
[26] M J Thomas, et al. Fatty Acid Composition of Low-Density Lipoprotein Influences Its Susceptibility to Autoxidation. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8110785/
[27] Jaume Marrugat, et al. Effects of Differing Phenolic Content in Dietary Olive Oils on Lipids and LDL Oxidation--A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur J Nutr. 2004 Jun. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15168036/
[28] Evangelia Tsartsou, et al. Network Meta-Analysis of Metabolic Effects of Olive-Oil in Humans Shows the Importance of Olive Oil Consumption With Moderate Polyphenol Levels as Part of the Mediterranean Diet. Front Nutr. 2019 Feb. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6379345/
[29] Álvaro Hernáez, et al. Olive Oil Polyphenols Decrease LDL Concentrations and LDL Atherogenicity in Men in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr. 2015 Aug. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4516770/
[30] Hicham Berrougui, et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Promote Cholesterol Efflux and Improve HDL Functionality. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015 Oct. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4606102/
[31] Nalini Kaul, et al. A Comparison of Fish Oil, Flaxseed Oil and Hempseed Oil Supplementation on Selected Parameters of Cardiovascular Health in Healthy Volunteers. J Am Coll Nutr. 2008 Feb. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18460481/
[32] Dianne A Hyson, et al. Almonds and Almond Oil Have Similar Effects on Plasma Lipids and LDL Oxidation in Healthy Men and Women. J Nutr. 2002 Apr. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11925464/
[33] Wayne H F Sutherland, et al. Effect of Meals Rich in Heated Olive and Safflower Oils on Oxidation of Postprandial Serum in Healthy Men. Atherosclerosis. 2002 Jan. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11755938/
[34] R Carmena, et al. Effect of Olive and Sunflower Oils on Low Density Lipoprotein Level, Composition, Size, Oxidation and Interaction With Arterial Proteoglycans. Atherosclerosis. 1996 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8842355/
[35] O Ezaki, et al. Long-term Effects of Dietary Alpha-Linolenic Acid From Perilla Oil on Serum Fatty Acids Composition and on the Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease in Japanese Elderly Subjects. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1999 Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10737229/
[36] Nina S Nielsen, et al. Different Effects of Diets Rich in Olive Oil, Rapeseed Oil and Sunflower-Seed Oil on Postprandial Lipid and Lipoprotein Concentrations and on Lipoprotein Oxidation Susceptibility. Br J Nutr. 2002 May. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12010587/
[37] Alberto Dávalos, et al. Red Grape Juice Polyphenols Alter Cholesterol Homeostasis and Increase LDL-receptor Activity in Human Cells in Vitro. J Nutr. 2006 Jul. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16772435/
[38] Shoko Kobayashi. The Effect of Polyphenols on Hypercholesterolemia through Inhibiting the Transport and Expression of Niemann–Pick C1-Like 1. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6801711/
[39] T J van Berkel, et al. LDL Receptor-Independent and -Dependent Uptake of Lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1995 Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8821464/
[40] G Jürgens, et al. Modification of Human Serum Low Density Lipoprotein by Oxidation--Characterization and Pathophysiological Implications. Chem Phys Lipids. Nov-Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3319231/
[41] Ari Palomäki, et al. Effects of Dietary Cold-Pressed Turnip Rapeseed Oil and Butter on Serum Lipids, Oxidized LDL and Arterial Elasticity in Men With Metabolic Syndrome. Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21122147/
[42] M Suzukawa, et al. Effects of Fish Oil Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Size, Oxidizability, and Uptake by Macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1995 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7775859/
[43] Marta Guasch-Ferré, et al. Olive oil intake and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in the PREDIMED Study. BMC Med. 2014 May. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4030221/
[44] Marta Guasch-Ferré, et al. Associations of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids From Plant and Animal Sources With Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in Two US Prospective Cohort Studies. Circ Res. 2019 Apr. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30689516/
[45] Pan Zhuang, et al. Dietary Fats in Relation to Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Prospective Cohort of 521 120 Individuals With 16 Years of Follow-Up. Circ Res. 2019 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30636521/
[46] Jingjing Jiao, et al. Dietary Fats and Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Analysis in Two Population Based Cohort Studies. BMJ. 2019 Jul. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31266749/
[47] Geng Zong, et al. Monounsaturated Fats From Plant and Animal Sources in Relation to Risk of Coronary Heart Disease Among US Men and Women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29566185/
[48] Lukas Schwingshackl, et al. Effects of Oils and Solid Fats on Blood Lipids: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J Lipid Res. 2018 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30006369/
[49] C Cox, et al. Effects of Dietary Coconut Oil, Butter and Safflower Oil on Plasma Lipids, Lipoproteins and Lathosterol Levels. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998 Sep. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9756121/
[50] Chenyan Lv, et al. Effects of dietary palm olein on the cardiovascular risk factors in healthy young adults. Food Nutr Res. 2018 Jul. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6052506/
[51] O A Tokede and J M Gaziano, L Djoussé. Effects of Cocoa Products/Dark Chocolate on Serum Lipids: A Meta-Analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2011 Aug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21559039/
[52] Farinaz Raziani, et al. Consumption of regular-fat vs reduced-fat cheese reveals gender-specific changes in LDL particle size - a randomized controlled trial. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018 Sep. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6150982/
[53] Fredrik Rosqvist, et al. Potential Role of Milk Fat Globule Membrane in Modulating Plasma Lipoproteins, Gene Expression, and Cholesterol Metabolism in Humans: A Randomized Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Jul. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26016870/
[54] James J DiNicolantonio and James H O’Keefe. Omega-6 vegetable oils as a driver of coronary heart disease: the oxidized linoleic acid hypothesis. Open Heart. 2018 Sep. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6196963/
[55] Dariush Mozaffarian, et al. Effects on Coronary Heart Disease of Increasing Polyunsaturated Fat in Place of Saturated Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS Med. 2010 Mar. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20351774/
[56] Maryam S Farvid, et al. Dietary Linoleic Acid and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Circulation. 2014 Oct. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25161045/
[57] Matti Marklund, et al. Biomarkers of Dietary Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. Circulation. 2019 May. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30971107/
[58] Wei-Sin Yang, et al. Association Between Plasma N-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in a Community-based Cohort Study. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31848413/















Do you think my theory on Sydney Heart Study holds weight?
ReplyDeleteThe reason for higher mortality in the PUFA group was due to them absolutely tanking the omega 3/6 ratio.
Were they having fish? Omega 3 rich foods?
Or was it lets call it 98% Omega 6's in their PUFA's.
Not even the ratio may matters if you are just having a reasonable level of Omega 3 in the diet to begin with. And I don't think they were.
My theory anyways. Happy to hear your thoughts.
Thanks for commenting. I don't really buy it, really. The ratio was a concept created by people who were worried that too much LA would produce too much arachidonic acid (AA). But pretty much every study on that subject has concluded that LA is not converted to AA at any rates that should make a ratio physiologically relevant at all. If the ratio matters, it is through a separate mechanism that has nothing to do with the original hypothesis.
Deletehttps://michaellustgarten.com/2020/12/15/ldl-cholesterol-whats-optimal-for-health-and-longevity/
ReplyDeleteHaving too low LDL cholesterol is (somehow) associated with higher mortality risks in the population, even in non-statin users.
MUFAs (when incorporated in cell membranes) might be slightly more prone to ROS-damage than SFAs (there was a study showing that longer-lived animal species tend to have the highest level of saturation in their cellular membranes). The body can convert SFAs to MUFAs via desaturase enzymes, but it doesn't have saturase enzymes to convert MUFAs to SFAs.
Thanks for this Tom.
ReplyDelete